A Complete Guide to Understanding Flow Meter Principles and Applications
Introduction: The Lifeline of Liquid and Gas Operations
Every time fuel is pumped, chemicals are dosed, or water is transferred, there’s a hidden hero ensuring accuracy behind the scenes—a flow meter. These devices are the backbone of modern fluid management. Whether you’re operating a fueling depot in California, managing water utilities in Texas, or dosing high-value chemicals in pharmaceuticals, your entire operation depends on reliable flow measurement.
But how does a flow meter work? What’s happening inside that metal housing? And how can you choose one that won’t let you down?
Let’s break it down in simple, professional language—complete with real-world examples and the benefits of sourcing from Flow Controls Metering LLC, a California-based leader in flow solutions.
What is a Flow Meter?
A flow meter is a precision instrument that measures the amount of fluid (liquid, gas, or steam) passing through a pipeline. This can be done by measuring:
- Volume (e.g., gallons or liters per minute)
- Mass (e.g., kilograms or pounds per hour)
- Velocity (e.g., meters per second)
Flow meters are used across every major industry—from oil & gas to food & beverage, from pharmaceuticals to irrigation.
How Does a Flow Meter Work? (Core Concepts)
✅ The Basic Working Principle
At its core, a flow meter uses either mechanical movement, electromagnetic induction, sound waves, or mass deflection to determine how much fluid passes through a system over time.
Depending on the meter type, the working mechanism will differ, but all meters typically have the following components:
- Flow channel or sensor
- Signal converter or transmitter
- Display or output interface
Let’s explore the most common types and their working principles.
🧩 1. Positive Displacement (PD) Flow Meters
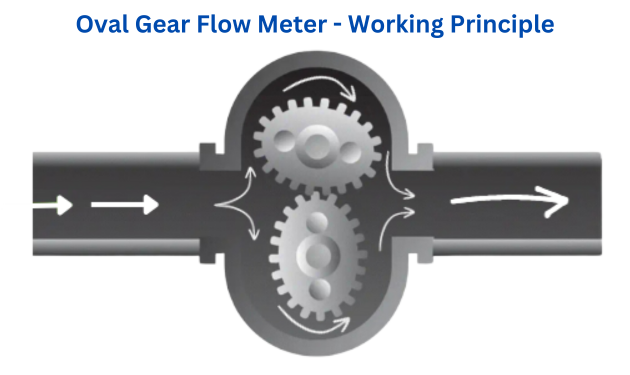
How It Works:
Fluid enters a chamber and physically moves mechanical parts (like gears, pistons, or disks). Each rotation or movement corresponds to a fixed volume. The meter counts these movements to determine flow.
Think of it like a fuel pump at a gas station.
Best Used For:
- Diesel, oil, fuels
- High-viscosity fluids
- Custody transfer applications
Flow Controls Model: FCM50 / FCM80 Series
Advantages:
- Exceptional accuracy (±0.2%)
- No need for external power
- Ideal for billing and invoicing
💨 2. Turbine Flow Meters
How It Works:
A rotor spins when fluid flows through it. The rotational speed is directly proportional to flow velocity. Sensors (typically magnetic or optical) count the blade passes.
Best Used For:
- Water, solvents, light oils
- HVAC systems
- General industrial fluids
Advantages:
- Economical and compact
- Good for steady, clean flows
- Fast response time
Image Suggestion:
Turbine flow meter close-up with visible rotor and pickup coil.
🔌 3. Electromagnetic (Mag) Flow Meters
How It Works:
Based on Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction. When a conductive fluid passes through a magnetic field inside the meter, it creates a voltage. This voltage is proportional to the fluid’s velocity.
Best Used For:
- Water, wastewater
- Slurries, sludges
- Conductive chemicals
Flow Controls Model: FCE Series
Advantages:
- No moving parts = minimal maintenance
- Excellent for corrosive or dirty fluids
- Works well with varying flow rates
🔊 4. Ultrasonic Flow Meters
How It Works:
Two transducers send sound waves through the fluid. The time it takes for the wave to travel upstream vs. downstream reveals the flow velocity. The difference is used to calculate flow rate.
Best Used For:
- Water, gases
- Non-intrusive applications
- Retrofit projects
Advantages:
- Clamp-on models require no pipe cutting
- Works with large pipe diameters
- Ideal for portable or temporary setups
⚖️ 5. Coriolis Mass Flow Meters
How It Works:
The meter vibrates a U-shaped tube. As fluid flows through, the Coriolis effect causes deflection in the tube. The amount of twist indicates mass flow rate. Some models also measure density and temperature.
Best Used For:
- Chemical batching
- Food & beverage
- Pharmaceuticals
Advantages:
- Direct mass flow measurement
- Ultra-high accuracy (±0.1%)
- Measures density and temp simultaneously
🧠 Modern Flow Meters = Smart Technology
Today’s flow meters aren’t just mechanical devices—they’re intelligent systems. Flow Controls’ meters support:
- RS485 / Modbus communication
- 4-20mA analog output
- Local display and totalizer
- Cloud dashboard integration
- Calibration logs and maintenance alerts
Whether you’re operating in a refinery or a remote water station, these digital capabilities allow for remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and compliance reporting.
Why Understanding Flow Meter Operation Matters
Knowing how a flow meter works is more than curiosity—it impacts your:
| Factor | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| ⚙️ Application Matching | Ensures you choose the right technology for your fluid |
| 🧪 Compliance | Regulatory bodies require traceable, calibrated measurements |
| 🧯 Safety | Avoids overflows, underdosing, and system failures |
| 💰 ROI | Accurate meters reduce waste, loss, and energy consumption |
Why Choose Flow Controls Metering LLC?
🌟 1. Expertly Engineered Products
Flow Controls meters are designed, tested, and calibrated to international standards. From our FCM positive displacement units to FCE electromagnetic meters, every unit is:
- Factory calibrated
- Precision machined
- Built for industrial resilience
🌍 2. Global Reach with Local Expertise
Though based in California, Flow Controls partners with global distributors like Ferindo Energi Instrumen (ferindo.id) in Southeast Asia. That means local service, faster delivery, and fluent support wherever you are.
📡 3. Smart Integration, Real-Time Data
All our digital meters can be connected to SCADA systems, cloud platforms, and automation networks. If your operations are headed toward Industry 4.0, we’ve already paved the way.
📋 4. Full Lifecycle Support
From product selection to on-site calibration, troubleshooting, and documentation compliance, our experts work with you every step of the way.
Real-World Success Story
🚛 Bulk Fuel Supplier – Arizona
Challenge: Inconsistent metering during fuel deliveries led to customer complaints and financial discrepancies.
Solution: Installed FCM80 PD Meters with digital totalizers and RS485 communication.
Outcome:
- Accuracy improved to ±0.2%
- Customer trust restored
- Integrated monitoring via web dashboard
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can flow meters be used on gases too?
A: Yes. Some flow meters like thermal mass or ultrasonic are designed for gas applications. Flow Controls focuses primarily on liquid meters but can advise on hybrid solutions.
Q: How do I know if my meter needs recalibration?
A: If your readings fluctuate or your totals don’t match expected volumes, it may be time. Flow Controls offers recalibration and certification services.
Q: Can one meter work for multiple fluids?
A: Possibly, but check material compatibility and recalibration needs. Our technical team can help you configure it safely.
Final Thoughts: Knowing How Flow Meters Work = Smarter Decisions
Flow meters aren’t just tools—they’re critical control points for modern industrial systems. Understanding how they work helps you make informed decisions, avoid costly errors, and drive real-world efficiency.
At Flow Controls Metering LLC, we don’t just provide equipment—we deliver accuracy, integration, and support.
📞 Ready to Improve Your Flow System?
Explore industry-grade flow meters at:
🔗 www.fcmeter.com
Need regional support in Southeast Asia?
🌍 ferindo.id
Flow Controls Metering LLC – Where Flow Meets Precision™
Sources & References
API MPMS Chapter 5 – Metering Systems